Product Overview
Vardenafil / Apomorphine HCl Troches are compounded sublingual dosage forms that combine two pharmacologically distinct agents-vardenafil, a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor, and apomorphine, a centrally acting dopamine D2-like receptor agonist-into a single moldable matrix intended to dissolve slowly under the tongue. Erectile dysfunction (ED) affects an estimated 150 million men worldwide, with prevalence projected to double by 2025, yet many patients respond incompletely to monotherapy. Clinical evaluation of vardenafil in men with diabetes demonstrated robust efficacy even in difficult-to-treat populations, underscoring its potential value when delivered in patient-friendly formats such as troches.[1]
Troches, also called medicated lozenges or pastilles, are solid oral preparations designed to remain in contact with the oral mucosa to facilitate transmucosal drug delivery; unlike conventional tablets they avoid first-pass hepatic metabolism and can be compounded in individualized strengths and flavor profiles. Modern base systems use polyethylene glycol or gelatin-sugar matrices to create dose-uniform units that soften but do not crumble at body temperature, enabling predictable release kinetics over several minutes. Quality-by-design principles recommend calibration of molds, monitoring of weight variation, and verification of active ingredient dispersion to maintain batch-to-batch consistency, procedures readily achievable in a 503A pharmacy environment.[2]
Combining a peripheral vasodilatory agent such as vardenafil with a centrally acting dopamine agonist addresses two complementary nodes of the erectile cascade, and a systematic review of randomized trials evaluating sublingual apomorphine demonstrated incremental improvements in intercourse success rates over placebo without disproportionate safety signals. When utilized alongside agents that amplify cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) signaling, dopaminergic stimulation may enhance libido-mediated cortical input, thereby lowering the threshold for erection in psychogenic and neurogenic subgroups. Early investigator-initiated case series of compounded dual-ingredient troches have further suggested rapid onset (typically < 15 minutes) and durable functional outcomes, although larger controlled studies are still warranted.[3]
Clinical trials employing flexible-dose protocols initiated vardenafil at 10 mg equivalents, titrating to 5 mg or 20 mg based on responsiveness and tolerability; success rates improved significantly across dosing strata without proportional rises in adverse effects. Compounded troches standardized at 40 mg vardenafil / 8 mg apomorphine can be divided into quarters to approximate 10 mg / 2 mg increments, granting prescribers granular control.[15]
Patients are instructed to place the troche beneath the tongue and allow it to dissolve completely over five to ten minutes, avoiding swallowing to maximize mucosal absorption. Onset is generally observed within fifteen minutes, with functional duration of approximately four hours. No more than one full troche should be used in a 24-hour period, and at least 24 hours should elapse between doses in those concurrently receiving moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors.[16]
Vardenafil selectively inhibits phosphodiesterase type 5, the enzyme responsible for cGMP degradation within cavernosal smooth muscle. In vitro assays demonstrated that vardenafil possesses a Ki approximately one order of magnitude lower than that of sildenafil, translating into potent potentiation of nitric-oxide mediated vasodilation, augmented intracavernosal pressure, and improved rigidity duration in human corpus cavernosum tissue and animal models.[4]
Apomorphine exerts pro-erectile effects through activation of hypothalamic and mesolimbic dopaminergic pathways, notably within the paraventricular nucleus where dopamine facilitates oxytocin release that subsequently triggers parasympathetic outflow to penile vascular beds. Pharmacokinetic profiling reveals rapid absorption via the sublingual route, peak plasma levels within twenty minutes, and extensive first-pass metabolism if swallowed, supporting buccal delivery systems such as troches. The compound’s pro-kinetic D2 activity accounts for its characteristic nausea, yet lower transmucosal doses markedly attenuate this liability.[5]
Translational data suggest synergism when central dopaminergic activation precedes or accompanies peripheral PDE5 inhibition. A recent meta-analysis comparing combination regimens to monotherapy demonstrated statistically significant gains in International Index of Erectile Function scores without material increases in adverse events, thereby endorsing dual-mechanism strategies for men refractory to single-agent therapy.[6]
The troche should not be prescribed to patients who are concurrently using any form of organic nitrates or nitric-oxide donors, nor to those with severe hypotension, uncontrolled arrhythmias, advanced heart failure, or recent myocardial infarction, as additive vasodilatory effects can precipitate profound blood-pressure reductions. A medication-interaction resource highlights that co-administration with select alpha-adrenergic blockers may also enhance orthostatic effects; clinicians are advised to ensure hemodynamic stability before initiating therapy.[7]
Cardiology-focused safety advisories further caution against using phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors within 24-48 hours of short-acting nitrates or within 48-72 hours of long-acting nitrate patches. In patients with coronary artery disease who require anti-anginal rescue therapy shortly after vardenafil exposure, hospital-based monitoring and alternate vasodilators such as non-nitrate agents are recommended. Similarly, sexual activity itself may impose unacceptable cardiac stress in those with unstable ischemic symptoms, rendering the product contraindicated until cardiovascular status is optimized.[8]
Apomorphine displays clinically meaningful pharmacodynamic interactions with serotonin 5-HT₃ receptor antagonists such as ondansetron, resulting in episodes of profound hypotension and syncope; this combination must be avoided. In addition, the emetic propensity of apomorphine may be exaggerated by dopamine-sensitizing anti-Parkinsonian regimens, whereas pre-treatment with peripherally acting dopamine antagonists-e.g., trimethobenzamide-can mitigate nausea without blunting efficacy.[9]
Vardenafil is primarily metabolized by cytochrome P450 3A4; potent inhibitors-including ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir, and clarithromycin-can elevate systemic exposure four- to eight-fold, necessitating dose reduction or avoidance. Conversely, strong inducers such as rifampin may diminish effectiveness. Concomitant ingestion with grapefruit products warrants caution due to pathway inhibition. The agent also prolongs the QT interval; concurrent use with class IA or class III antiarrhythmics should therefore be approached judiciously.[10]
Most men tolerate the vardenafil component well; headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and dyspepsia predominate and are typically mild and transient. Visual disturbances, principally blue-tinted vision, occur less frequently than with sildenafil, yet rare reports of non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy exist. Post-marketing surveillance indicates no clinically meaningful effect on spermatogenesis, testosterone levels, or prostate size.[11]
Apomorphine-related adverse reactions mirror its dopaminergic profile, with dose-dependent nausea, yawning, dizziness, and somnolence being most common. Sublingual delivery circumvents peak plasma spikes associated with parenteral formulations, thereby reducing emesis; still, pretreatment with peripheral dopamine antagonists may be prudent in sensitive individuals. Reports of mild transient hypotension underscore the need for initial administration under supervision, particularly in patients on antihypertensives.[12]
Although animal studies administering vardenafil at exposures up to one-hundred-fold higher than human therapeutic levels showed no teratogenicity, the product is categorized as Pregnancy Category B under legacy criteria and is not indicated for women. Limited clinical experience, combined with potential systemic vasodilatory and hemodynamic effects, dictates avoidance during pregnancy.[13]
A widely used pharmaceutical compendium similarly notes absence of controlled data in pregnant or lactating populations and advises that therapy be reserved exclusively for male patients. Women who may inadvertently come into contact with the medication-such as caregivers handling troches-should observe standard precautions, including wearing gloves to minimize dermal exposure.[14]
Finished troches should be dispensed in airtight, light-resistant containers and stored at controlled room temperature between 20 °C and 25 °C. Studies examining common household heat excursions highlight the risk of potency loss when medicines are exposed to sustained temperatures above 30 °C; patients should therefore avoid leaving the product in vehicles or near heat sources.[17]
Compounding records emphasize the importance of moisture control, as polyethylene glycol bases can absorb ambient humidity and alter dissolution profiles. Mold calibration data suggest less than five-percent weight variability when troches are wrapped in foil pouches immediately after cooling and kept below 25 °C. Refrigeration is not required and may induce condensation upon warming, potentially compromising structural integrity.[1]
- Goldstein, I., Young, J. M., Fischer, J., Bangerter, K., Segerson, T., Taylor, T., et al. (2003). Vardenafil, a new phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor, in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes: A multicenter double-blind placebo-controlled fixed-dose study. Diabetes Care, 26(3), 777-783. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.26.3.777
- Anusha, P., Yadav, G., & Kumar, R. (2021). Lozenges formulation and evaluation: A review. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Science Archive, 7(1), 15-22. https://www.pharmacyjournal.net/assets/archives/2022/vol7issue1/7-1-15-242.pdf
- Guillén, V., Rueda, J. R., Lopez-Argumedo, M., Solà, I., & Ballesteros, J. (2020). Apomorphine for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 49, 2963-2979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10508-020-01817-5
- Saenz de Tejada, I., Angulo, J., Cuevas, P., Fernández, A., Moncada, I., et al. (2001). The phosphodiesterase inhibitory selectivity and in vivo potency of the new PDE5 inhibitor vardenafil. International Journal of Impotence Research, 13, 282-290. https://www.nature.com/articles/3900726.pdf
- Auffret, M., Drapier, S., & Vérin, M. (2018). The many faces of apomorphine: Lessons from the past and challenges for the future. Drugs in R&D, 18(2), 91-107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-018-0619-3
- Mykoniatis, I., Skriapas, K., & colleagues. (2021). Combination therapy for erectile dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Network Open, 4(2), e2039654. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.39654
- Sohal, M., & Ulrich, A. (2024). Seven vardenafil interactions you can avoid. GoodRx Health. https://www.goodrx.com/vardenafil/interactions
- The Cardiology Advisor. (2024). Erectile dysfunction drugs and nitrates: A dangerous combination. The Cardiology Advisor. https://www.thecardiologyadvisor.com/features/erectile-dysfunction-drugs-and-nitrates/
- Drugs.com. (2025). Apomorphine-uses, dosage, side effects, warnings. https://www.drugs.com/apomorphine.html
- Patel, N. (2018). Oral phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction. U.S. Pharmacist, 43(6), 26-33. https://www.uspharmacist.com/article/oral-pde5-inhibitors-for-erectile-dysfunction
- Wood, S. (2024). Levitra versus Viagra: Comparing two ED drugs. Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/levitra-vardenafil-vs-viagra-sildenafil-for-ed-8644413
- Wagner, G., et al. (2002). The role of sublingual apomorphine in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. European Urology Supplements, 1(2), 71-77. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1569-9056(02)00008-8
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2024). Levitra (vardenafil HCl) Prescribing Information. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2008/021400s011lbl.pdf
- Drugs.com. (2025). Vardenafil use during pregnancy. https://www.drugs.com/pregnancy/vardenafil.html
- Porst, H., et al. (2004). The efficacy and safety of flexible-dose vardenafil in a broad population of men with erectile dysfunction. European Urology, 45(4), 620-628. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0302-2838(04)00020-X
- Eden Health. (2025). Vardenafil dosage guide. https://www.tryeden.com/post/vardenafil-dosage
- Christodoulopoulos, G. (2025). Medication storage: Temperature guidelines and how to deal with excursions. GoodRx Health. https://www.goodrx.com/drugs/medication-basics/medication-storage-temperature-guidelines
- University of North Carolina Eshelman School of Pharmacy. (2015). Morphine troches formulation record. https://pharmlabs.unc.edu/wp-storage/labs/formulation_records/morphine_troches_form.pdf
- Neumeyer, J. L., & Perry, B. D. (1978). Stability of apomorphine in solutions containing ascorbic acid and sodium bisulfite. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 67(3), 379-382. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3549(15)43350-7
- Liu, R., et al. (2021). The effect of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors on erectile function recovery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 12, 735708. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.735708
- Hellstrom, W. J., & Sikka, S. C. (2003). Vardenafil: A novel type 5 phosphodiesterase inhibitor for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Current Urology Reports, 4(5), 473-481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-003-0030-2
- Corona, G., et al. (2015). Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: A comprehensive review. European Urology, 68(1), 104-115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2015.06.038
- United States Pharmacopeia. (2023). <1079> Good storage and shipping practices. https://ftp.uspbpep.com/v29240/usp29nf24s0_c1079.html
- Medication Training UK. (2023). Medicines storage in a heatwave. https://medicationtraining.co.uk/medicines-storage-in-a-heatwave/
- Hims Health. (2023). Apomorphine for erectile dysfunction: Does it work? https://www.hims.com/blog/apomorphine-for-ed
- Dinsmore, W., & Wyllie, M. (2000). Apomorphine: An update of clinical trial results. International Journal of Impotence Research, 12(Suppl 4), S151-S155. https://www.nature.com/articles/3900581.pdf
- Ralph, D. J., et al. (2010). Inhalation device allows novel administration of apomorphine in men with erectile dysfunction. Journal of Sexual Medicine, 7(4 Pt 1), 1508-1517. https://academic.oup.com/jsm/article/7/4_part_1/1508/6848920
- UroToday. (2020). Apomorphine for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: Systematic review and meta-analysis. https://www.urotoday.com/recent-abstracts/men-s-health/erectile-dysfunction/124942-apomorphine-for-the-treatment-of-erectile-dysfunction-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis.html
Is the combination suitable for patients with diabetes?
Systematic evaluations indicate that phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors improve endothelial function and erectile parameters even in men with long-standing diabetes, and synergy with central agents may further enhance response rates without glycemic destabilization.[20]
Does vardenafil work faster than sildenafil?
Comparative pharmacodynamic studies suggest that vardenafil achieves maximal plasma concentrations within forty-five minutes and may demonstrate higher in-vitro potency, translating into a slightly quicker onset for some users, though individual variability remains significant.[21]
Can alcohol be consumed with the troche?
Moderate alcohol intake did not meaningfully alter vardenafil pharmacokinetics in controlled studies, but excessive consumption can heighten vasodilatory effects and impair erectile performance; limiting intake to one-to-two standard drinks is advisable.[22]
What happens if the product freezes during shipping?
Pharmacopeial storage standards classify controlled room temperature as 20 °C-25 °C with transient excursions; freezing may cause cracking and non-uniform dissolution, so any troches that have been frozen solid should be inspected and replaced if distorted.[23]
Is it safe to carry troches while traveling in hot climates?
Consumer-level studies of temperature excursions reveal that medicine pouches left in parked cars can exceed 50 °C within an hour; using insulated containers and air-conditioned storage markedly reduces degradation risk.[24]
Why might apomorphine cause yawning?
Central dopamine receptor activation can trigger hypothalamic circuits associated with yawning and drowsiness; these effects are benign and tend to diminish after repeated exposure or dose reduction.[25]
How many doses of apomorphine have been studied in clinical trials?
Phase III programs have administered more than 75,000 sublingual doses to over 3,000 participants, establishing a well-characterized safety database for short-acting usage patterns.[26]
Are inhaled formulations interchangeable with troches?
Investigational dry-powder inhalers delivering microgram quantities of apomorphine demonstrated dose-dependent efficacy but utilize distinct pharmacokinetic profiles and have not been evaluated in combination with vardenafil; substitution is therefore not recommended.[27]
Is the combination appropriate after prostate surgery?
Meta-analytic data suggest that apomorphine’s efficacy may be attenuated in men who have undergone radical prostatectomy, yet coupling with a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor can still yield clinically meaningful improvements in selected cases under specialist supervision.[28]
Disclaimer: This compounded medication is prepared under section 503A of the U.S. Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Safety and efficacy for this formulation have not been evaluated by the FDA. Therapy should be initiated and monitored only by qualified healthcare professionals.
Administration Instructions
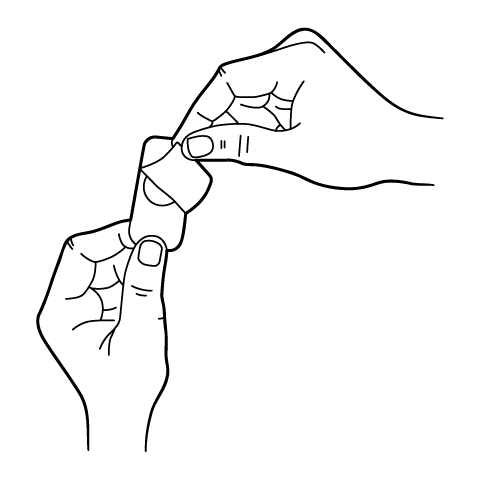
ODT and Troches Instructions
503A vs 503B
- 503A pharmacies compound products for specific patients whose prescriptions are sent by their healthcare provider.
- 503B outsourcing facilities compound products on a larger scale (bulk amounts) for healthcare providers to have on hand and administer to patients in their offices.
Frequently asked questions
Our team of experts has the answers you're looking for.
A clinical pharmacist cannot recommend a specific doctor. Because we are licensed in all 50 states*, we can accept prescriptions from many licensed prescribers if the prescription is written within their scope of practice and with a valid patient-practitioner relationship.
*Licensing is subject to change.
Each injectable IV product will have the osmolarity listed on the label located on the vial.

Given the vastness and uniqueness of individualized compounded formulations, it is impossible to list every potential compound we offer. To inquire if we currently carry or can compound your prescription, please fill out the form located on our Contact page or call us at (877) 562-8577.
We source all our medications and active pharmaceutical ingredients from FDA-registered suppliers and manufacturers.

 Sildenafil / Apomorphine HCl Troches
Sildenafil / Apomorphine HCl Troches Tadalafil / Phentolamine Mesylate Capsules
Tadalafil / Phentolamine Mesylate Capsules Sildenafil / Oxytocin ODT
Sildenafil / Oxytocin ODT Tadalafil / Oxytocin ODT
Tadalafil / Oxytocin ODT Tadalafil Troches
Tadalafil Troches Tadalafil ODT
Tadalafil ODT Tadalafil / Tramadol HCl Troches
Tadalafil / Tramadol HCl Troches Tadalafil / Apomorphine HCl Troches
Tadalafil / Apomorphine HCl Troches