Coenzyme Q10 (Ubidecarenone) Injection
Product Overview
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) Injection is a compounded prescription medication containing the antioxidant coenzyme Q10 as the active ingredient. It is typically formulated at a concentration of 20 mg/mL in a 10 mL vial with a grapeseed oil base for intramuscular use.[1] As a 503A or 503B compounded preparation, it is made on a prescription or office use basis for patients under U.S. FDA regulations.[9]
CoQ10 is a fat-soluble, vitamin-like coenzyme found naturally in every cell, with especially high levels in energy-intensive organs like the heart, liver, and kidneys. It plays a critical role in cellular energy production by facilitating electron transfer within mitochondria, and it also functions as a potent antioxidant.[2][3]
Clinically, CoQ10 supplementation has been explored for a wide range of conditions related to suboptimal cellular energy metabolism and oxidative stress. It is often used as an adjunct to support cardiovascular health (e.g. in heart failure or cardiomyopathy), neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, migraines, and certain fertility or metabolic conditions.[2][3]
However, CoQ10 lacks FDA approval for the treatment of any specific medical condition and current research evidence for its efficacy in many of these uses remains inconclusive. Nonetheless, it is generally regarded as a well-tolerated supplement and is commonly recommended by healthcare providers in appropriate scenarios.[2][4]
There is no one-size-fits-all dosage for CoQ10 Injection; the dose and frequency are individualized based on the patient’s needs and the treating provider’s discretion. The compounded injection is available as 20 mg/mL in a 10 mL vial, and it is intended for intramuscular administration (intravenous use of this oil-based formulation is contraindicated). In practice, a common regimen might involve injecting 1 mL (20 mg of CoQ10) intramuscularly once or twice per week, or as directed by the healthcare provider, although dosing can vary widely with clinical context. Therapy is typically started at a low dose to gauge tolerance, and the dose or frequency may be adjusted according to the patient’s response and CoQ10 blood levels if those are being monitored.
For comparison, oral CoQ10 supplementation in adults often ranges from about 50 mg to 300 mg per day (in divided doses) for general health support, and much higher doses (hundreds of milligrams daily) have been used in clinical trials for specific conditions like Parkinson’s disease or mitochondrial disorders.[2][3] Because intramuscular injection bypasses the digestive system, it achieves 100 % bioavailability of CoQ10, so doses by injection may be lower than equivalent oral doses.
Nonetheless, no official standardized dosing exists for the injectable form, and clinicians will tailor the dosing schedule to the individual patient. Patients should always follow the dosing instructions provided by their prescriber. CoQ10’s effects on the body are gradual, so therapy may be continued for several weeks or months, with periodic re-evaluation of the patient’s condition and CoQ10 levels as needed to determine the optimal dosage and duration of treatment.
CoQ10 is integral to the mechanism of cellular energy production. It serves as a coenzyme in the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation pathway, shuttling electrons between complexes I/II and complex III of the electron transport chain to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP).[2][3] In doing so, CoQ10 helps maintain efficient energy output in cells.
Beyond its bioenergetic role, CoQ10 in its reduced form (ubiquinol) acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage by scavenging free radicals and preventing lipid peroxidation. It also stabilizes membranes and supports endothelial function by preserving nitric oxide availability, thereby contributing to improved blood flow.[4]
Through these actions, CoQ10 Injection can bolster cellular energy levels and reduce oxidative stress, which is particularly beneficial in conditions associated with CoQ10 deficiency or high oxidative demand.[2][3]
CoQ10 Injection has no known absolute contraindications apart from hypersensitivity to CoQ10 itself or any of the formulation’s components. Patients with a history of allergic reactions to coenzyme Q10 or to excipients (such as the grapeseed oil vehicle) should not use this therapy.[2][3]
While not absolute contraindications, caution is advised in certain populations due to limited data: for example, its use in very young pediatric patients or in individuals with specific medical conditions should be guided by a physician’s judgement.
In all cases, CoQ10 should be avoided in anyone who has demonstrated an allergy to this compound or similar quinones in the past.
CoQ10 may interact with several medications, so a healthcare provider should review all concurrent drugs before initiating therapy. Notably, CoQ10 can diminish the effectiveness of warfarin and other anticoagulants: because CoQ10 is structurally similar to vitamin K, it may reduce warfarin’s anticoagulation effect, potentially increasing the risk of blood clots.[4][5] Patients on warfarin should have their coagulation parameters closely monitored if CoQ10 is started or adjusted.
CoQ10 also has mild blood pressure-lowering properties and can have an additive effect with antihypertensive medications, possibly leading to excessive drops in blood pressure.[4] Similarly, CoQ10 might enhance the blood-sugar-lowering effects of insulin or oral hypoglycemic drugs, so glucose levels should be watched in diabetic patients.[5]
There is also a theoretical concern that CoQ10’s antioxidant effects could interfere with certain chemotherapy or radiation treatments, so patients undergoing cancer therapy should use CoQ10 only under medical supervision.[5]
In summary, while serious drug interactions are uncommon, CoQ10 users should consult their healthcare provider, as dosage adjustments or enhanced monitoring may be necessary when combining CoQ10 with blood thinners, blood pressure medications, diabetes medications, or cancer therapies.[4][5]
CoQ10 Injection is generally well tolerated.[5] Most side effects, if they occur, tend to be mild and transient. Commonly reported side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, stomach upset, diarrhea, or loss of appetite.[4][5]
Some individuals have noted central nervous system-related symptoms like headache, dizziness, or mild insomnia, especially at higher doses. Occasional skin reactions (rashes or itching) have been observed in a few cases.[4]
Because this formulation is administered by intramuscular injection, there can also be localized injection site reactions, such as pain, redness, or bruising at the injection site (as with any intramuscular shot).
Overall, the incidence of side effects is low: large studies and reviews have found CoQ10 to be a compound with a favorable side effect profile.[2][4] Patients are advised to report any unexpected or persistent adverse effects to their healthcare provider.
Use of CoQ10 Injection during pregnancy requires caution due to insufficient research on its safety in pregnant or nursing women.[6][7] CoQ10 is classified as a dietary supplement and has not been studied in large clinical trials for safety in pregnancy. While no teratogenic or toxic effects have been reported in the limited human data available, the evidence is not sufficient to consider it definitively safe for expectant mothers.[6]
Some small studies of oral CoQ10 supplementation in pregnancy (for example, in women at risk for pre-eclampsia) have suggested potential benefits and did not identify safety concerns, but these results are preliminary and not conclusive. Therefore, CoQ10 should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk, and always under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.[6]
The same precaution applies to breastfeeding: it is unknown whether significant amounts of CoQ10 could be transferred through breast milk, so nursing mothers should consult their physicians before using CoQ10.
In summary, until more data are available, CoQ10 in any form is generally not recommended in pregnant or breastfeeding patients unless specifically prescribed by a physician after careful risk-benefit assessment.[6][7]
Proper storage of CoQ10 Injection helps maintain its potency and sterility. Vials should be stored at controlled room temperature, typically around 20-25°C (68-77°F), and kept away from excessive heat, direct light, and moisture.[7][8] Do not freeze the vial, as freezing can damage the oil-based formulation.
It is best to keep the medication in its original amber vial (to protect from light) and in a dry place. Always check the expiration or beyond-use date provided by the compounding pharmacy, and do not use the product beyond that date. Once a vial is punctured, follow your pharmacist’s guidance on how long it may be safely used (some compounded sterile preparations may have a limited usable period after first use).
Keep CoQ10 vials out of reach of children and store them securely to prevent any contamination. Before each use, inspect the solution: if you notice particulate matter, cloudiness, or any change in color from its normal appearance, do not use the vial and contact the pharmacy.
By adhering to storage recommendations, patients can ensure the medication remains stable and effective for the duration of its intended use.[7][8]
- Defy Medical. (2020). Coenzyme Q10 20 mg/mL injectable, 10 mL (Grapeseed Oil) [Product information]. Defy Medical Store. (Available from: https://www.defymedicalstore.com/coq10*).*
- Bonakdar, R. A., & Guarneri, E. (2005). Coenzyme Q10. American Family Physician, 72(6), 1065-1070.
- Sood, B., & Patel, P. (2023). Coenzyme Q10. In StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing. (Available from NCBI Bookshelf: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531491*).*
- Merck & Co., Inc. (n.d.). Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). Merck Manual - Consumer Version. (Retrieved May 27, 2025, from: https://www.merckmanuals.com/home/special-subjects/dietary-supplements-and-vitamins/coenzyme-q10-coq10*).*
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. (2019, January). Coenzyme Q10. National Institutes of Health. (Retrieved from: https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/coenzyme-q10*).*
- RxList Inc. (n.d.). Coenzyme Q10: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions and Warnings. RxList Online Drug Information. (Retrieved May 27, 2025, from: https://www.rxlist.com/coenzyme_q10/generic-drug.htm*).*
- Drugs..com. (2023, August 23). Coenzyme Q10: Uses, Side Effects & Dosage. (Retrieved from: https://www.drugs.com/coenzyme-q10.html*).*
- ColumbiaDoctors. (n.d.). Coenzyme Q10 (ubidecarenone) - oral. Columbia University Irving Medical Center Health Library. (Retrieved from: https://www.columbiadoctors.org/health-library/drug-info/coenzyme-q10-ubidecarenone-oral*).*
- The FDA Group. (2021, November 16). 503A vs. 503B: A quick-guide to compounding pharmacy designations & regulations. (Retrieved from: https://www.thefdagroup.com/blog/503a-vs-503b-compounding-pharmacies*).*
What is Coenzyme Q10 (Ubidecarenone) Injection and what is it used for?
Coenzyme Q10 Injection is a specialized compounded formulation of the nutrient CoQ10, intended to deliver this substance directly into the body via intramuscular injection. It is used to increase CoQ10 levels in individuals who might benefit from its potential effects on cellular energy production and antioxidant support.
Doctors may recommend CoQ10 injections for patients with certain conditions characterized by low CoQ10 or high oxidative stress; for example, some practitioners use it as an adjunct for heart failure, chronic fatigue, neurodegenerative diseases, or in patients experiencing statin-related muscle symptoms, among other uses.[2][3]
It’s important to note that while CoQ10 has shown promise in various small studies, its use is generally as a supportive therapy and not a primary treatment for any disease.[2][4] Always consult a healthcare provider to determine if CoQ10 Injection is appropriate for a specific condition.
How does CoQ10 Injection work in the body?
CoQ10 Injection works by delivering coenzyme Q10 directly into the bloodstream and then to the cells, where it can exert its physiological effects. CoQ10 itself is a crucial coenzyme in mitochondria, the energy powerhouses of cells, so it helps cells produce ATP (energy) more efficiently by participating in the electron transport chain.[2][3]
In addition, CoQ10 is a powerful antioxidant. This means it helps neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative damage in cells.[4] By improving mitochondrial energy generation and protecting cells from oxidative stress, CoQ10 can support the normal function of high-energy tissues like the heart and muscles.
Patients who are deficient in CoQ10 or have increased needs (due to illness or medication use) may experience an improvement in energy levels, exercise tolerance, or other symptoms when their CoQ10 levels are restored toward normal. The injectable form ensures that CoQ10 is readily absorbed and delivered to tissues, bypassing any absorption issues that can occur with oral supplements.
How is CoQ10 Injection administered?
CoQ10 Injection is given into muscle, usually as an intramuscular (IM) injection. A common site for IM injection is the upper thigh or gluteal (hip) muscle. The injection comes in a multi-dose vial (10 mL vial at 20 mg/mL concentration), and a healthcare professional will instruct you on the proper technique if you are administering it at home.
Typically, a dose (often 1 mL, which contains 20 mg of CoQ10) is drawn up in a syringe and injected into the muscle tissue. Injections may be administered on a schedule such as once or twice per week, or as prescribed, depending on your particular needs. The IM route allows the CoQ10 to be absorbed steadily into the circulation.
It’s important to rotate injection sites (if you are doing frequent injections) to minimize local irritation. Because this product is compounded under prescription, you should follow the dosing and administration plan given by your provider and not exceed the recommended dose.
CoQ10 Injection should not be given intravenously; the grapeseed oil formulation is intended for IM use only and intravenous injection could cause serious complications. If you have any concerns about how to inject or feel uncomfortable doing it yourself, arrange for administration by a healthcare professional.
What are the benefits of CoQ10 injections versus oral CoQ10 supplements?
The primary benefit of CoQ10 injections is enhanced bioavailability. When CoQ10 is given by intramuscular injection, it bypasses the digestive system and first-pass metabolism, meaning the full dose is made available to the body. Oral CoQ10 supplements, by contrast, must be absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, and CoQ10’s absorption can be variable and sometimes poor (especially if not taken with fat, since it is fat-soluble).
Injections can achieve higher and more consistent blood levels of CoQ10, which may be advantageous in cases where robust supplementation is needed. Additionally, for patients who cannot tolerate oral supplements or have malabsorption issues (such as certain gastrointestinal disorders or after bariatric surgery), injections provide an effective alternative.
Clinically, some patients report improvements in energy, stamina, or symptom relief (for example, less muscle fatigue) when receiving CoQ10 injections, particularly if they had low CoQ10 levels to begin with. It’s important to manage expectations, however: CoQ10 is a supplement to support cellular function and is not a stimulant, so the benefits may be subtle or gradual.
The decision to use injection over oral form depends on individual patient factors and should be guided by a healthcare provider.
What side effects should I watch out for?
CoQ10 is generally very well tolerated, but like any supplement or medication it can cause some side effects in certain individuals. The side effects of CoQ10 injections are usually mild. You might experience some soreness or redness at the injection site; this is a common side effect of any intramuscular injection.
Systemically, possible side effects include digestive issues (such as nausea, upset stomach, or diarrhea) and occasionally headaches or insomnia.[4][5] Some people have reported skin rashes or itching, but serious allergic reactions are very rare.[4] If you notice swelling, hives, or difficulty breathing (signs of an allergic reaction) after a CoQ10 injection, seek medical attention immediately.
Also, if you experience symptoms like severe dizziness, chest pain, or any concerning change after your injection, contact your doctor. However, these are uncommon outcomes. Most patients do not have significant side effects from CoQ10.
To minimize stomach-related side effects, even though the injection bypasses the gut, ensure you’re staying hydrated and injecting properly. Overall, CoQ10’s safety profile is excellent; in fact, no serious long-term adverse effects have been definitively linked to CoQ10 in studies.[5] Always report any bothersome or persistent side effects to your healthcare provider, as they can determine if CoQ10 or something else is the cause and adjust your regimen if necessary.
Can CoQ10 injections interact with my other medications?
Yes, CoQ10 can interact with certain medications, so it’s important to let your healthcare provider know about all drugs and supplements you are taking.[4][5] One of the most important interactions is with blood thinners like warfarin. CoQ10 may reduce the effectiveness of warfarin, leading to a lower INR and a higher risk of clotting.[4] If you are on warfarin, your doctor may need to monitor you more frequently or adjust your dose when starting or stopping CoQ10.
CoQ10 may also have additive effects with blood pressure medications; since it can modestly lower blood pressure on its own, taking it alongside antihypertensive drugs might result in blood pressure that’s too low in some cases.[4] Similarly, CoQ10 might enhance the glucose-lowering effect of insulin or certain diabetes medications, so blood sugar should be watched to avoid hypoglycemia.[5]
There is also a potential interaction with cancer treatments: because CoQ10 is an antioxidant, there’s a theoretical concern it could interfere with chemotherapy or radiation therapy (which often rely on oxidative damage to kill cancer cells).[5] If you are undergoing cancer treatment, always discuss with your oncologist before using CoQ10 or any supplement.
In general, CoQ10 has a low interaction profile and is considered acceptable to use with most medications, but these specific interactions are noteworthy. Always keep your healthcare team informed about your CoQ10 use so they can manage any interactions proactively.
Do I need a prescription for CoQ10 Injection?
Yes. CoQ10 Injection is not an over-the-counter product; it is a compounded medication that must be prescribed by a licensed healthcare provider. Under Section 503A and 503B of the U.S. Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, compounding pharmacies and outsourcing facilities can prepare medications like CoQ10 Injection only in response to an individual prescription for a specific patient or for office use.[9]
This means you cannot purchase CoQ10 Injection off the shelf or online without a prescription. If you and your doctor decide that CoQ10 injections are appropriate for you, your doctor will write a prescription that is sent to a compounding pharmacy. The pharmacy will then compound (mix) the CoQ10 Injection according to strict quality standards and dispense it to you.
It’s also worth noting that insurance coverage for compounded medications varies; some plans may not cover CoQ10 injections since they are not commercially manufactured products, so be sure to check with your insurer.
Always use a reputable compounding pharmacy that follows USP <797> guidelines for sterile compounding or an outsourcing facility that utilizes cGMP standards, to ensure you receive a quality product. If you have further questions about access or cost, discuss them with your healthcare provider or pharmacist when considering CoQ10 Injection therapy.
Administration Instructions
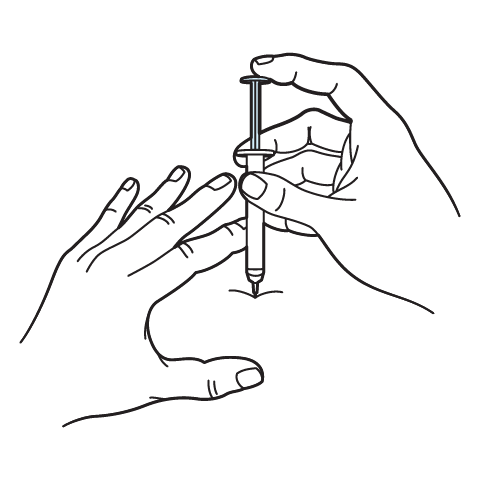
Intramuscular Injection Instructions
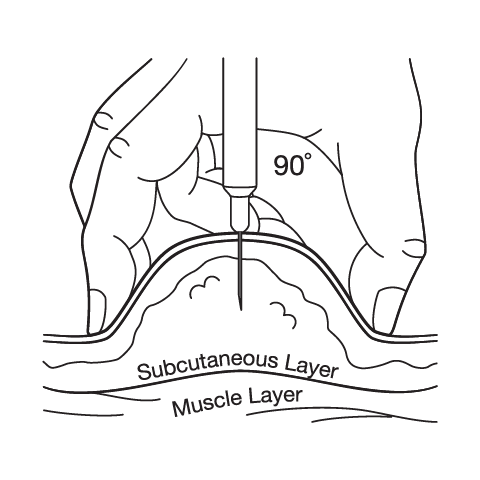
Subcutaneous Injection Instructions
503A vs 503B
- 503A pharmacies compound products for specific patients whose prescriptions are sent by their healthcare provider.
- 503B outsourcing facilities compound products on a larger scale (bulk amounts) for healthcare providers to have on hand and administer to patients in their offices.
Frequently asked questions
Our team of experts has the answers you're looking for.
A clinical pharmacist cannot recommend a specific doctor. Because we are licensed in all 50 states*, we can accept prescriptions from many licensed prescribers if the prescription is written within their scope of practice and with a valid patient-practitioner relationship.
*Licensing is subject to change.
Each injectable IV product will have the osmolarity listed on the label located on the vial.

Given the vastness and uniqueness of individualized compounded formulations, it is impossible to list every potential compound we offer. To inquire if we currently carry or can compound your prescription, please fill out the form located on our Contact page or call us at (877) 562-8577.
We source all our medications and active pharmaceutical ingredients from FDA-registered suppliers and manufacturers.


 Coenzyme Q10 Capsules
Coenzyme Q10 Capsules Zinc Sulfate Injection
Zinc Sulfate Injection Magnesium Chloride Injection
Magnesium Chloride Injection Methylcobalamin Injection (Vitamin B12)
Methylcobalamin Injection (Vitamin B12) Hydroxocobalamin (Vitamin B12) Injection
Hydroxocobalamin (Vitamin B12) Injection Cholecalciferol (D3) Injection
Cholecalciferol (D3) Injection